- Print Markdown To Pdf
- Markdown To Pdf Npm
- Generate Pdf From Markdown Word
- Generate Pdf From Markdown Python
- Generate Pdf From Markdown Files
In the previous tutorials we’ve learned about the R Markdown format and how to create a report using R Markdown in RStudio. In this tutorial, we will render or knit an R Markdown document to a web friendly, html format using the Rknitr package. knitr can be used to convert R Markdown files to many different formats including: html, pdf, GitHub markdown (.md) and more.
Learning Objectives
Print Markdown To Pdf
At the end of this lesson, you will:
- Be able to produce (
knit) anhtmlfile from anR Markdownfile. - Know how to modify chuck options to change what is rendered and not rendered on the output
htmlfile.
What You Need
How to generate a PDF from a Markdown file — using Node.js and JavaScript Summary: Translating Markdown to PDF is an essential part of many report generation systems. PDF is a portable format that can enable users to share files on mediuns such as. Pandoc options input-file. Pandoc is a Haskell library for converting from one markup format to another, and a command-line tool that uses this library. Pandoc can convert between numerous markup and word processing formats, including, but not limited to, various flavors of Markdown, HTML, LaTeX and Word docx.For the full lists of input and output. Pip install pdfkit markdown. Here's some example code to take a Markdown source file and write a PDF file. If your source is HTML, you can skip the step converting the source Markdown. From markdown import markdown import pdfkit inputfilename = 'README.md' outputfilename = 'README.pdf' with open (inputfilename, 'r') as f: htmltext. Via a Visual Studio Code extension (tested in 2020) Download the Yzane Markdown PDF extension. Right click inside a Markdown file ( md) The content below will appear. Select the Markdown PDF: Export (pdf) option. Note: Emojis are better in Windows than Linux (I don't know why) Share. Improve this answer.
You will need the most current version of R and, preferably, RStudio loaded on your computer to complete this tutorial. You will also need an R Markdown document that contains a YAML header, code chunks and markdown segments.
Install R Packages
- knitr:
install.packages('knitr') - rmarkdown:
install.packages('rmarkdown')
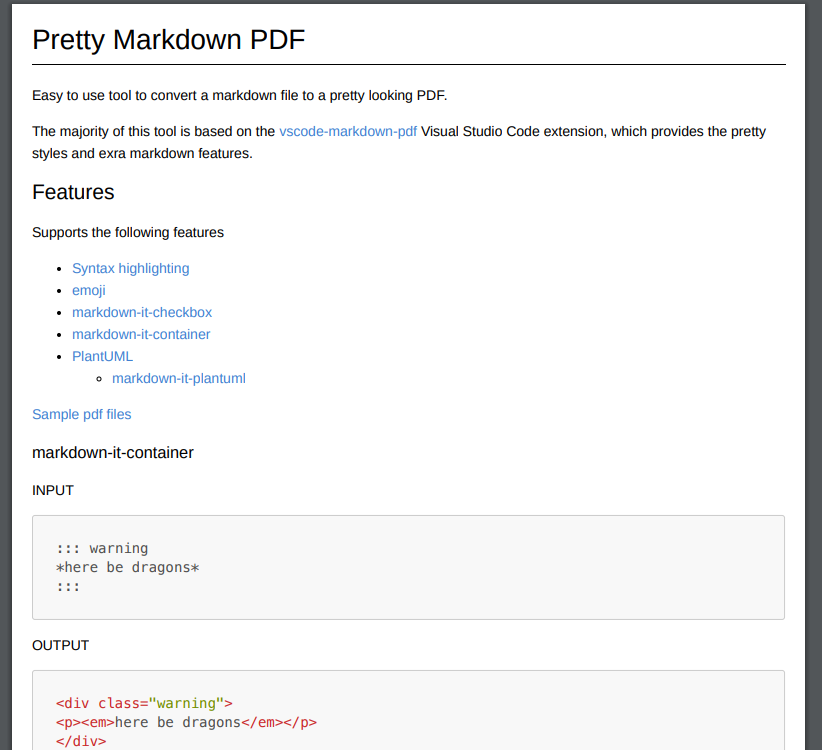
What is Knitr?
knitr is the R package that we use to convert an R Markdown document into another, more user friendly format like .html or .pdf.
The knitr package allows us to:
- Publish & share preliminary results with collaborators.
- Create professional reports that document our workflow and results directly from our code, reducing the risk of accidental copy and paste or transcription errors.
- Document our workflow to facilitate reproducibility.
- Efficiently change code outputs (figures, files) given changes in the data, methods, etc.
The knitr package was designed to be a transparent engine for dynamic report generation with R – Yihui Xi – knitr package creator
When To Knit: Knitting is a useful exercise throughout your scientific workflow. It allows you to see what your outputs look like and also to test that your code runs without errors. The time required to knit depends on the length and complexity of the script and the size of your data.
How to Knit
To knit in RStudio, click the Knit pull down button. Ap llr test questions in telugu pdf. You want to use the Knit HTML option for this lesson.
When you click the Knit HTML button, a window will open in your console titled R Markdown. This pane shows the knitting progress. The output (html in this case) file will automatically be saved in the current working directory. If there is an error in the code, an error message will appear with a line number in the R Console to help you diagnose the problem.
Data tip: You can run knitr from the command prompt using: render(“input.Rmd”, “all”).
View the Output
When knitting is complete, the html file produced will automatically open.
Notice that information from the YAML header (title, author, date) is printed at the top of the HTML document. Then the html shows the text, code, and results of the code that you included in the Rmd document.
Challenge Activity
Add the code below to your .Rmd document. Then knit to .html format.
When you knit your .Rmd file to pdf, the plot you produce should look like the one below. Not so pretty, eh? Don’t worry - we will learn more about plotting in a later tutorial!
Where is the File?
In the steps above, we downloaded a file. However, where did that file go on your computer? Let’s find it before we go any further.
Is the boulder-precip.csv file there?

Either you've already heard of pandoc or if you have searched online for markdown to pdf or similar, you are sure to come across pandoc. This tutorial will help you use pandoc to generate pdf and epub from a GitHub style markdown file. The main motivation for this blog post is to highlight what customizations I did to generate pdf and epub versions for self-publishing my ebooks. It wasn't easy to arrive at the set-up I ended up with, so I hope this will be useful for those looking to use pandoc to generate pdf and epub formats. This guide is specifically aimed at technical books that has code snippets.
Installation🔗
If you use a debian based distro like Ubuntu, the below steps are enough for the demos in this tutorial. Algebra abstracta de herstein pdf. If you get an error or warning, search that issue online and you'll likely find what else has to be installed.
I first downloaded deb file from pandoc: releases and installed it. Followed by packages needed for pdf generation.
For more details and guide for other OS, refer to pandoc: installation
Minimal example🔗

Markdown To Pdf Npm
Once pandoc is working on your system, try generating a sample pdf without any customization.
See learnbyexample.github.io repo for all the input and output files referred in this tutorial.
Here sample_1.md is input markdown file and -f is used to specify that the input format is GitHub style markdown. The -o option specifies the output file type based on extension. The default output is probably good enough. But I wished to customize hyperlinks, inline code style, add page breaks between chapters, etc. This blog post will discuss these customizations one by one.
pandoc has its own flavor of markdown with many useful extensions — see pandoc: pandocs-markdown for details. GitHub style markdown is recommended if you wish to use the same source (or with minor changes) in multiple places.
It is advised to use markdown headers in order without skipping — for example, H1 for chapter heading and H2 for chapter sub-section, etc is fine. H1 for chapter heading and H3 for sub-section is not. Using the former can give automatic index navigation on ebook readers.
On Evince reader, the index navigation for above sample looks like this:
Chapter breaks🔗
As observed from previous demo, by default there are no chapter breaks. Searching for a solution online, I got this piece of tex code:
This can be added using -H option. From pandoc manual,
-H FILE, --include-in-header=FILE
Include contents of FILE, verbatim, at the end of the header. Thiscan be used, for example, to include special CSS or JavaScript inHTML documents. This option can be used repeatedly to include multiplefiles in the header. They will be included in the order specified.Implies --standalone.
The pandoc invocation now looks like:
You can add further customization to headings, for example use sectionfont{underlineclearpage} to underline chapter names or sectionfont{LARGEclearpage} to allow chapter names to get even bigger. Here's some more links to read about various customizations:
Changing settings via -V option🔗
-V KEY[=VAL], --variable=KEY[:VAL]
Set the template variable KEY to the value VAL when rendering thedocument in standalone mode. This is generally only useful when the--template option is used to specify a custom template, since pandocautomatically sets the variables used in the default templates. Ifno VAL is specified, the key will be given the value true.
The -V option allows to change variable values to customize settings like page size, font, link color, etc. As more settings are changed, better to use a simple script to call pandoc instead of typing the whole command on terminal.
mainfontis for normal textmonofontis for code snippetsgeometryfor page size and marginslinkcolorto set hyperlink color- to increase default font size, use
-V fontsize=12pt- See stackoverflow: change font size if you need even bigger size options
Using xelatex as the pdf-engine allows to use any font installed in the system. One reason I chose DejaVu was because it supported Greek and other Unicode characters that were causing error with other fonts. See tex.stackexchange: Using XeLaTeX instead of pdfLaTeX for some more details.
The pandoc invocation is now through a script:
Do compare the pdf generated side by side with previous output before proceeding.
On my system, DejaVu Serif did not have italic variation installed, so I had to use sudo apt install ttf-dejavu-extra to get it.
Syntax highlighting🔗
One option to customize syntax highlighting for code snippets is to save one of the pandoc themes and editing it. See stackoverflow: What are the available syntax highlighters? for available themes and more details (as a good practice on stackoverflow, go through all answers and comments — the linked/related sections on sidebar are useful as well).
Edit the above file to customize the theme. Use sites like colorhexa to help with color choices, hex values, etc. For this demo, the below settings are changed:
Inline code
Similar to changing background color for code snippets, I found a solution online to change background color for inline code snippets.
Add --highlight-style pygments.theme and --include-in-header inline_code.tex to the script and generate the pdf again.
With pandoc sample_2.md -f gfm -o sample_2.pdf the output would be:
With ./md2pdf_syn.sh sample_2.md sample_2_syn.pdf the output is:
For my Python re(gex)? book, by chance I found that using ruby instead of python for REPL code snippets syntax highlighting was better. Snapshot from ./md2pdf_syn.sh sample_3.md sample_3.pdf result is shown below. For python directive, string output gets treated as a comment and color for boolean values isn't easy to distinguish from string values. The ruby directive treats string value as expected and boolean values are easier to spot.
Generate Pdf From Markdown Word

Bullet styling🔗
This stackoverflow Q&A helped for bullet styling.
Comparing pandoc sample_4.md -f gfm -o sample_4.pdf vs ./md2pdf_syn_bullet.sh sample_4.md sample_4_bullet.pdf gives:
PDF properties🔗
This tex.stackexchange Q&A helped to change metadata. See also pspdfkit: What’s Hiding in Your PDF? and discussion on HN. Dell b1165nfw driver.
./md2pdf_syn_bullet_prop.sh sample_4.md sample_4_bullet_prop.pdf gives:
Adding table of contents🔗
There's a handy option --toc to automatically include table of contents at top of the generated pdf. You can control number of levels using --toc-depth option, the default is 3 levels. You can also change the default string Contents to something else using -V toc-title option.
./md2pdf_syn_bullet_prop_toc.sh sample_1.md sample_1_toc.pdf gives:
Adding cover image🔗
To add something prior to table of contents, cover image for example, you can use a tex file and include it verbatim. Create a tex file (named as cover.tex here) with content as shown below:
Then, modify the previous script md2pdf_syn_bullet_prop_toc.sh by adding --include-before-body cover.tex and tada — you get the cover image before table of contents. thispagestyle{empty} helps to avoid page number on the cover page, see also tex.stackexchange: clear page.
The bash script invocation is now ./md2pdf_syn_bullet_prop_toc_cover.sh sample_5.md sample_5.pdf.
You'll need at least one image in input markdown file, otherwise settings won't apply to the cover image and you may end up with weird output. sample_5.md used in the command above includes an image. And be careful to use escapes if the image path can contain tex metacharacters.
Stylish blockquote🔗
By default, blockquotes (lines starting with > in markdown) are just indented in the pdf output. To make them standout, tex.stackexchange: change the background color and border of blockquote helped.
Create quote.tex with the contents as shown below. You can change the colors to suit your own preferred style.
Generate Pdf From Markdown Python
The bash script invocation is now ./md2pdf_syn_bullet_prop_toc_cover_quote.sh sample_5.md sample_5_quote.pdf. The difference between default and styled blockquote is shown below.
Customizing epub🔗
For a long time, I thought epub didn't make sense for programming books. Turned out, I wasn't using the right ebook readers. FBReader is good for novels but not ebooks with code snippets. When I used atril and calibre ebook-viewer, the results were good.
I didn't know how to use css before trying to generate the epub version. Somehow, I managed to take the default epub.css provided by pandoc and customize it as close as possible to the pdf version. The modified epub.css is available from the learnbyexample.github.io repo. The bash script to generate the epub is shown below and invoked as ./md2epub.sh sample_5.md sample_5.epub. Note that pygments.theme is same as the pdf customization discussed before.
Resource links🔗
More options and workflows for generating ebooks:
- pandoc-latex-template — a clean pandoc LaTeX template to convert your markdown files to PDF or LaTeX
- Jupyter Book — open source project for building beautiful, publication-quality books and documents from computational material
- See also fastdoc — the output of fastdoc is an asciidoc file for each input notebook. You can then use asciidoctor to convert that to HTML, DocBook, epub, mobi, and so forth
- Asciidoctor
- Sphinx
Miscellaneous
Generate Pdf From Markdown Files
- picular: search engine for colors and colorhexa